1- Iran boasts the second largest economy in the Middle East, following Saudi Arabia. With an estimated nominal GDP of USD 413.49 billion in 2022, the nation’s economic potential is significant.
In 2014, Iran experienced a growth rate of 4.3%, as reported by the World Bank. Looking ahead, Iran aims for an ambitious 8% annual GDP growth up to 2028, although non-Iranian estimates suggest a more moderate growth rate of around 5% per year.
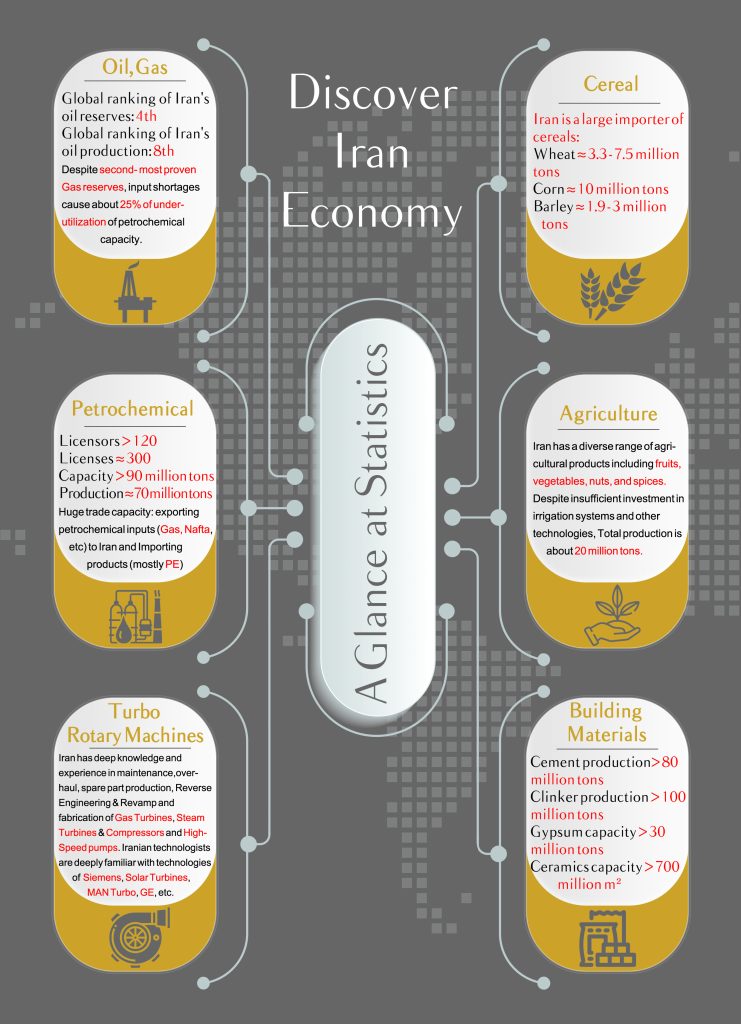
2- Iran’s economic structure is largely regulated by the state, which also holds substantial ownership in key industries such as extraction and manufacturing. Notably, entities owned by state-related organizations dominate the economic landscape, with true private sector companies accounting for only around 20% of economic activity.
Despite this dominance, Iran’s economy displays diversity, with significant presence in sectors such as oil and gas, mining, manufacturing, agriculture, and services. The nation boasts the world’s seventh-largest mineral reserves and a sizable consumer market, complemented by a robust industrial manufacturing base.
3- Some challenges persist in Iran’s labor market, characterized by a youthful, educated workforce juxtaposed with high unemployment rates, standing at 9.6% in 2022. Female labor force participation remains low, with only 14.6% of women active in the workforce. Moreover, minimum wages fall below international standards, recorded at USD 170 per month in 2014.
Investors eyeing Iran’s market may face hurdles, including the necessity to invest significantly in local staff training. Economic isolation in recent years has resulted in deviations from international best practices, particularly in technology-dependent sectors like oil and gas. Nevertheless, the Iranian government is actively addressing these issues to enhance compliance with international standards.